The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea of 10 December 1982 applies to ships navigating in international waters.
Article 98 of the UNCLOS provides that (1) Every State shall require the master of a ship flying its flag, in so far as he can do so without serious danger to the ship, the crew or the passengers (a) to render assistance to any person found at sea in danger of being lost and; (b) to proceed with all possible speed to the rescue of persons in distress, if informed of their need of assistance, in so far as such action may reasonably be expected of him;
On March 10, 2012, Jeff Gilligan of Portland, Oregon, was on The Star Princess, a luxury cruise ship operated by Carnival Cruise Lines, based out of Miami, Florida. Jeff is an avid bird watcher and that day he was bird watching with two fellow cruise passengers, using their binoculars and spotting telescopes from one of the decks of the ship.
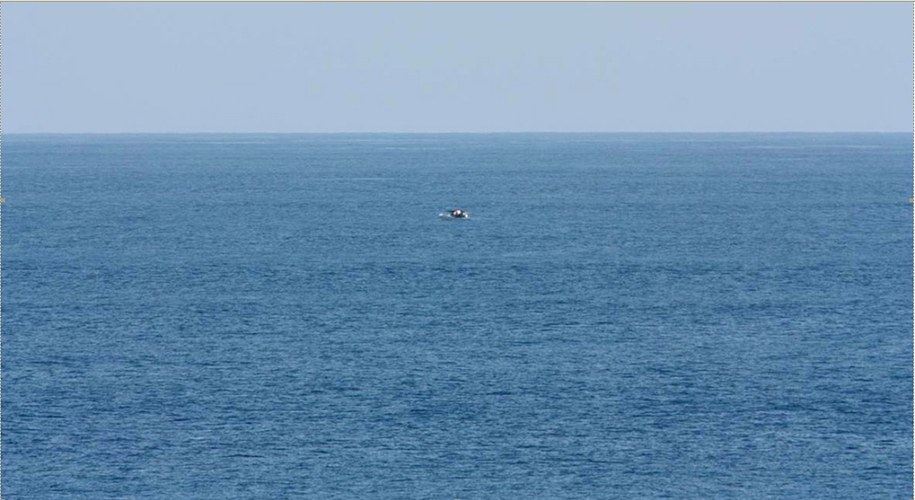
That is when Jeff and his two friends spotted a boat approximately one mile from the cruise ship. Using his binoculars, Jeff saw that the occupants on that small vessel were waving their t-shirts in the direction of the cruise ship. Jeff took a photo of the vessel.
Judy Meredith from Bend, Oregon, was with Jeff and told NPR: “We all watched him for a bit and thought, ‘This guy’s in distress. He’s trying to get our attention. And he doesn’t have a motor on his boat.’ We could see that.”
She then ran inside to alert the crew, but she only found a crew member who was with the ship’s sales team. The cruise employee contacted the bridge and the situation was relayed to the captain. Jeff Gilligan handed his telescope to another crew member to look at the drifting boat and he confirmed that he saw a boat in distress.
Jeff, Judy and the third bird-watcher thought the ship’s captain would either turn around to rescue the boaters or take the appropriate steps to ensure that the local authorities would conduct a rescue mission. Unfortunately, nothing was ever done.
Days after the cruise ended, Judy Meredith contacted Princess Cruise to inquire about what had happened to the boaters and the steps taken by the ship’s captain at the time. Judy’s tenacity was not something Princess Cruise was prepared for and several versions of the incident surfaced. The last version given by Princess was that cruise ship contacted the boaters in question, but rather than signaling for distress, they had been signaling for the ship to change course because they were afraid the large cruise ship would damage the boaters’ fishing nets. Also, Judy was told that what she mistakenly interpreted as boaters waving their t-shirts in a sign of distress was actually a sign of gratitude for having altered the ship’s course.
The three bird-watchers eventually found out several weeks later that the Ecuadorean coast guard had rescued a drifting fishing boat near the Galapagos Islands. On board, the rescuers found one survivor, Adrian Vasquez, 18, and two dead people, Oropeces Betancourt, 24, and Fernando Osario, 16.
Upon the flooding of reports that The Star Princess’ captain was made aware of the situation and that no rescue efforts were made to potentially save the lives of three stranded boaters in the middle of the pacific ocean, Princess Cruise and Carnival Cruise Lines have opened an internal investigation to look into the matter.
If the three bird-watchers’ version of what happened is verified, Princess Cruise would have violated international maritime law.
 Cruise Ship Lawyers Blog
Cruise Ship Lawyers Blog