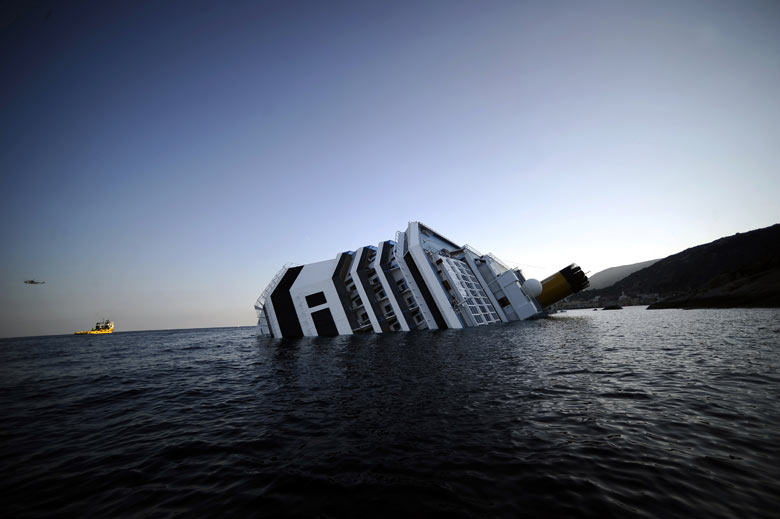
 The Athens Convention establishes a comprehensive integrated system to govern the liability of cruise ship operators for personal injuries and property damage sustained by its passengers. It contains standards for establishing liability and permissible defenses as well as its own statute of limitations and venue provisions. The Convention was primarily motivated by a series of uninsured ferry disasters occurring in a number of underdeveloped countries.
The Athens Convention establishes a comprehensive integrated system to govern the liability of cruise ship operators for personal injuries and property damage sustained by its passengers. It contains standards for establishing liability and permissible defenses as well as its own statute of limitations and venue provisions. The Convention was primarily motivated by a series of uninsured ferry disasters occurring in a number of underdeveloped countries.
Amid the Costa Concordia tragedy, it seems very likely that cruise passengers will have to file any lawsuits in Genoa, Italy, where the cases will be subject to Italian law. Courts in the United States have consistently upheld the choice of law clauses contained in cruise passenger tickets absent evidence that “enforcement would be unreasonable and unjust”, ” the clause was invalid for such reasons as fraud or overreaching”, or “the enforcement would contravene a strong public policy of the forum in which the suit is brought”.
More importantly, as part of this comprehensive system, the Athens Convention allows the carrier to limit its liability for passenger personal injury or death in the absence of its reckless misconduct. The current monetary limitation in U.S. dollar is approximately $72,000. The operative words are “in the absence of [the carrier’s] reckless misconduct.” Specifically, Article 13 of the Athens Convention provides that the carrier will lose its right to limit liability where it is proven that the damage resulted from an act or omission done with intent to cause damage or recklessly and with the knowledge that such damage would probably result.
Can Costa Concordia Passengers prove that the carrier acted recklessly and with knowledge that damage would probably result and lift the carrier’s right to limit its liability?
Here are the pertinent facts that have come to light thus far:
The cruise ship deviated from its original course
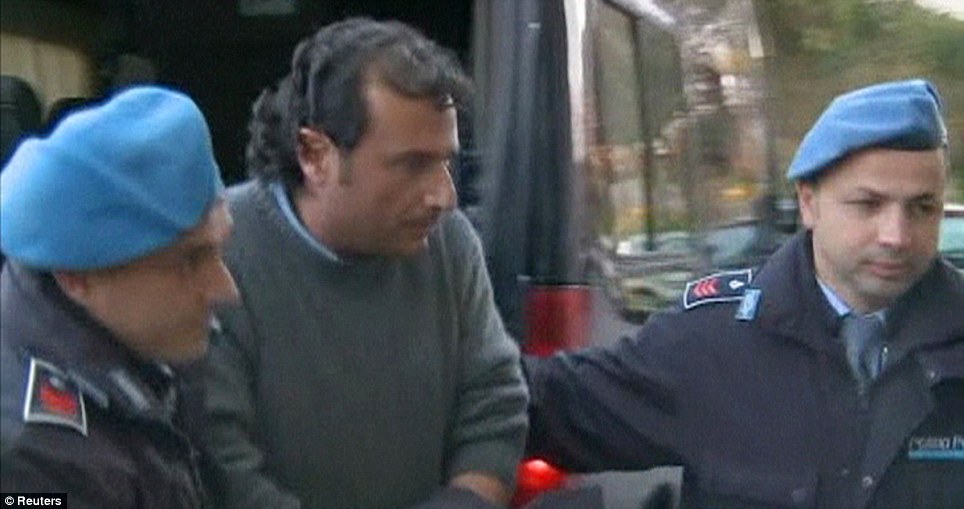
According to court documents filed today in Italy, Captain Francesco Schettino admitted to a judge that he made a mistake in steering the ship too close to the Island of Giglio. Captain Schettino deviated from the ship’s programmed route and came 0.28 nautical miles (less than 600 yards) from the coast.
The cruise ship intentionally deviated from its original course
Head waiter, Antonello Tievolli, reportedly did not ask the captain to steer towards his native island, but he nonetheless told his family that he would be passing by that evening and his sister, Patrizia Tievoli, shared his whereabouts on her Facebook profile by posting the following wall post: “In a short period of time the Concordia ship will pass very close. A big greeting to my brother who finally get to have a holiday on landing in Savona”.
Captain Francesco Schettino abandoned ship
According to an audio recording, which is now part of the prosecutor’s case against Captain Schettino who is currently under house arrest and facing criminal charges for manslaughter and for abandoning ship, it is established that the ship’s captain did leave the cruise liner before all passengers were evacuated and ashore.
The cruise company confirmed ship’s deviation was not authorized
Pier Luigi Foschi, chairman of Carnival’s Italian unit, Costa Crociere confirmed at a press conference in Genoa on January 16, that the Costa Concordia ran aground at about 9:45 p.m. on January 13, within hours of leaving a port near Rome to continue a Mediterranean cruise. The ship’s route was set electronically before it left, and the cruise liner should not have been so close to Giglio Island. Foshi added “the fact that the ship strayed from that course can only be due to a maneuver that was not approved, not authorized nor communicated to Costa Crociere by the captain of the ship”.
The cruise company knew of the common practice to sail close to the Island of Giglio
It has now surfaced that it was common practice for the Costa Concordia to deviate from its original route and to sail dangerously close to Giglio Island. An amateur video footage was recently posted online showing the Costa Concordia sailing off the coast of the island, closer to the shore in August 2011 than it did on January 13.
Italian Prosecutor qualifies Captain’s Schettino’s behavior as reckless
In a recent interview to the media, Italian Prosecutor Francesco Verusio declared that “the unscrupulousness of this reckless maneuver that the commander of the Costa Concordia made near the Island of Giglio is something that is inexcusable. From the investigation we carried out straight off the incident, we are certain that the captain of the ship was on the command bridge and the control of the ship was in his hands. This risky maneuver that the captain performed sailing close to Giglio Island without due caution caused the impact that we all saw. The captain is in a very difficult position because we are sure that he abandoned the ship when many passengers were still waiting to be evacuated”.
Continue reading
 Cruise Ship Lawyers Blog
Cruise Ship Lawyers Blog

 Port Authority: Speak in a loud voice.
Port Authority: Speak in a loud voice.

 According to several accounts from evacuated passengers, and as was confirmed by prosecutors, evidence is mounting that the ship’s captain was evacuated ashore, safe and sound, hours before hundreds of passengers even made it to a lifeboat.
According to several accounts from evacuated passengers, and as was confirmed by prosecutors, evidence is mounting that the ship’s captain was evacuated ashore, safe and sound, hours before hundreds of passengers even made it to a lifeboat.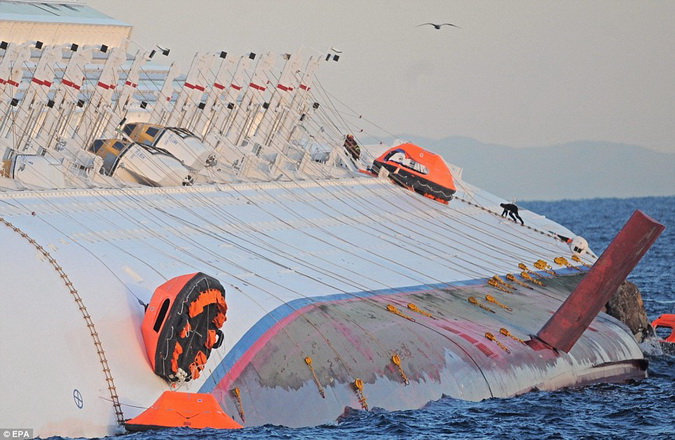
 According to the
According to the 