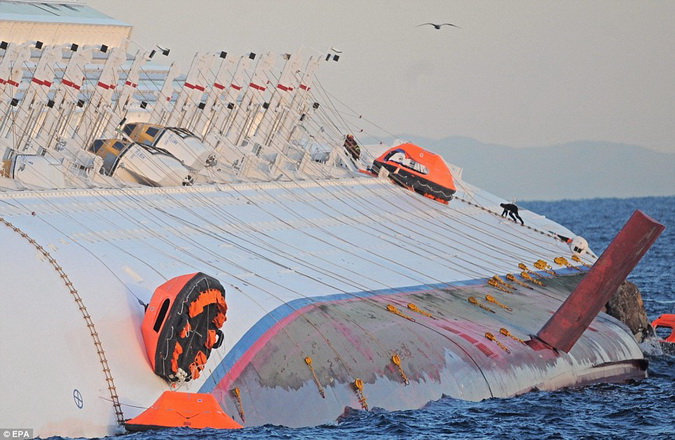
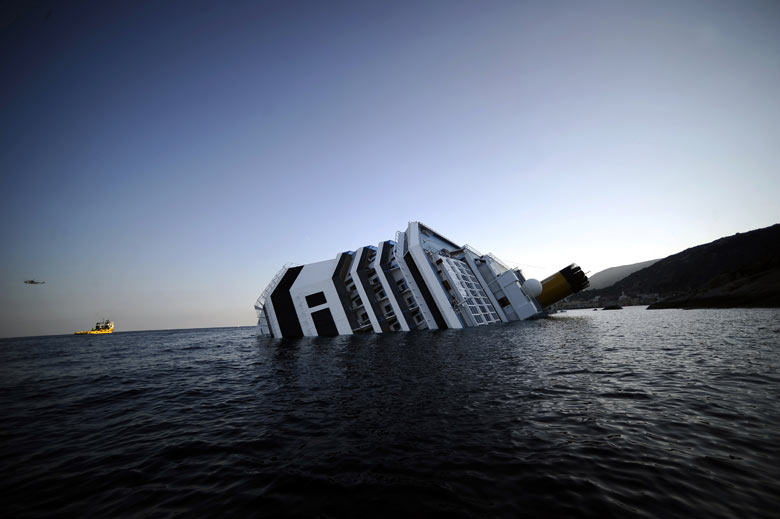
We began reporting on the Costa Concordia as soon as the tragedy occurred on Friday, January 13th, 2012. That night, thousands of passengers lived through a collective nightmare which ended in the most blatant mishandling of an emergency aboard a large cruise ship since the Titanic. Every single passenger aboard the Costa Cruise thought they were going to die at sea. Ultimately thirty-two passengers perished that night.
Four passengers currently in litigation provided a unique insight into what passengers aboard a stranded and sinking cruise ship were thinking and experiencing. What became crystal clear is the breakdown in communication and level of negligence displayed by Costa Cruise Lines employees of all rank.
Our four passengers were traveling together as a group and thankfully escaped the sinking ship. All four owe their luck to self-reliance and the common-sense of ignoring what Costa Cruise crew members were ordering passengers to do.
At approximately 9:00 p.m., all four friends met for dinner in the fourth floor dining room, where they were seated at the lower level. Shortly after they sat down, the ship suddenly tilted to one side, knocking over some glasses and plates. Everyone, passengers and crew-members alike, was stunned, however, within a couple of minutes, the restaurant patrons were assured by the dining staff that there was no problem.
Only minutes later, the ship sharply tilted to an extreme angle, sending all of the dishes and food on their table to the floor. This scene was replayed across the entire dining room as dishes and plates went flying everywhere. The angle of the ship was so severe that even tables were sliding across the floor, bringing to their minds the movie scenes of the sinking Titanic, which was the only cruising experience three of them had at the time.
Massive panic in the dining room broke out as families and friends attempted to protect children and loved ones and to make their way to safety through the chaos without any help from the staff.
After receiving no assistance or instruction from the staff, our group of friends quickly determined that they could not rely upon the ship’s personnel and would have to take the appropriate steps to save themselves. Remembering having seen life jackets in their closets, they fought their way through the flying china, furniture and panicking passengers out of the dining room, further impaired by the severe angle of the ship, which had also caused water to flood out of the galley on to the floor. After escaping from the dining room, one of the four friends became separated in the madness from the other three, who managed to stay together until the end.
The now smaller group fought its way through the maddening crowd of screaming, running and panicked passengers. One of them, a female passenger, slid in water which flooded out of the galley, turning the polished floor in the foyer outside of the dining room into an ice rink. As she slid across the tilted foyer, she only came to a stop after bashing into a metal column in the center. After someone helped her up, she continued to run through the chaos in an effort to catch up with her two other friends.
As they continued to run toward their cabins, they were all terrified and feared that the ship was going to sink. Since none of them were good swimmers, they all were afraid that if they had to jump overboard without a life jacket, their chances of survival were poor.
Continue reading
 Cruise Ship Lawyers Blog
Cruise Ship Lawyers Blog


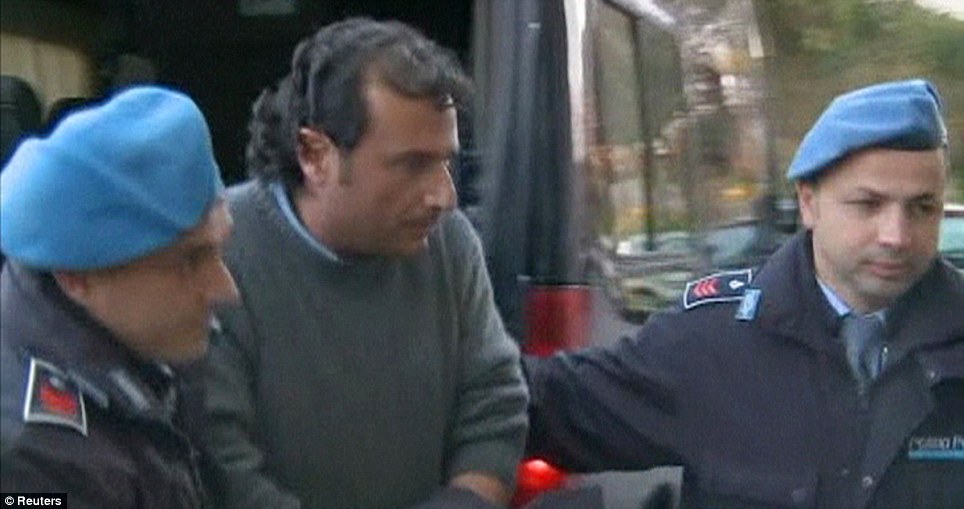
 The latest information coming out of the office of Italian prosecutor Francesco Verusio is the most damning evidence of recklessness yet on the part of Captain Schettino.
The latest information coming out of the office of Italian prosecutor Francesco Verusio is the most damning evidence of recklessness yet on the part of Captain Schettino.
 Port Authority: Speak in a loud voice.
Port Authority: Speak in a loud voice.

 According to several accounts from evacuated passengers, and as was confirmed by prosecutors, evidence is mounting that the ship’s captain was evacuated ashore, safe and sound, hours before hundreds of passengers even made it to a lifeboat.
According to several accounts from evacuated passengers, and as was confirmed by prosecutors, evidence is mounting that the ship’s captain was evacuated ashore, safe and sound, hours before hundreds of passengers even made it to a lifeboat.
